Home / Drug & Alcohol Rehab Programs Across New England / Cocaine Addiction: Learn about Cocaine Abuse
All types of drug addiction are a disease that have harmful effects on individuals. Those who stigmatize the issue are likely unaware of the physical changes in the brain that addiction causes. It’s these changes in the brain that make it hard for a person to quit. Cocaine use doesn’t take long to turn into an addiction because it’s a highly addictive substance. Some people become addicted the first time they use the drug. Signs of cocaine addiction include cravings, thinking about how to get more, lying or stealing money to get more cocaine and failing to uphold responsibilities.
If you suspect your loved one is using cocaine, look for the following signs of cocaine use:
Between 400,000 to 500,000 emergency room visits each year in the U.S. are from cocaine. There has been a rise in cocaine-related deaths and hospitalizations since 2017. From 2015 to 2016, cocaine-related deaths increased by 52.4%. In 2015, 13.2% of adults among the 45–54 age group of cocaine users were hospitalized because of a cocaine overdose, and 9.2% of adults among the 35–44 age group were hospitalized. Just over 10,600 people died from cocaine overdose in 2016, which was almost twice as many compared to cocaine overdose deaths from 2012.

How do you know if you or your loved one is having an overdose? Symptoms of a cocaine overdose:
An overdose of cocaine often ends in heart attack or stroke. It’s important that you go to a hospital if you suspect you or someone you know is experiencing an overdose. Injecting the drug carries a higher risk of overdose than snorting.
Many people who use cocaine also use another drug like alcohol, marijuana, heroin or prescription painkillers. This increases their chance of overdose and can cause additional health complications.
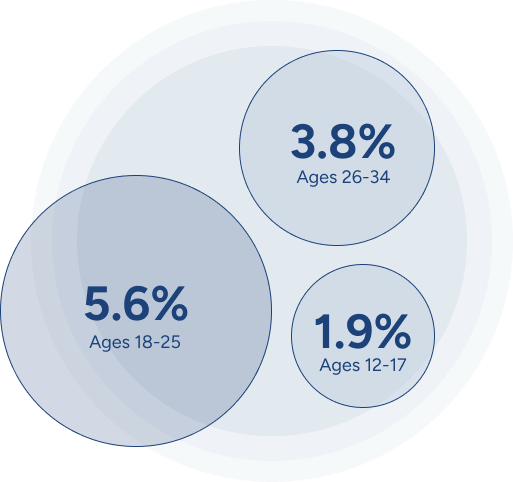
The CDC reported that 5.6% of people from ages 18 to 25 were using cocaine in 2016; 3.8% of people from ages 26 to 34 were using cocaine, and 1.9% of minors from ages 12 to 17 used cocaine. In general, cocaine use is less prevalent among teenagers because of its cost, but some teens are still able to get access to it whether through friends or other means.
Nearly 5 million Americans admitted to cocaine use in 2016. This is around 2% of the population, a statistic that hasn’t changed much over the years. According to Addiction Center, up to 1,800 Americans try cocaine each day. This is more than half a million people over the course of a year.
The good news is that law enforcement has been seizing higher amounts of cocaine since 2006, which has helped prevent more people from falling victim to this drug. The market size of cocaine has decreased since 2006 too. By playing our role in spreading information about the dangers of cocaine, we hope to see cocaine use and overdose statistics go down.
Cocaine is highly addictive and very dangerous. Using cocaine once can make someone addicted. This drug has a vicious cycle of making users feel depressed and even physically unwell after the high wears off. Craving more of the drug is another symptom of cocaine withdrawal. Mix these symptoms together, and you can see how easy it is for someone to take another dose in order to feel better. Cocaine use alters the brain in a physical way and hijacks the reward and pleasure centers. Activities you used to enjoy may no longer be enjoyable as a result.
Although all forms of cocaine are dangerous to your health, crack is the most dangerous because you don’t know how much you’re taking. Even if someone monitors how much they take with powder cocaine, an overdose is possible. People often develop a tolerance to the drug and need to take more over time to achieve the same high they desire.
Health problems caused by cocaine:
The drug can also cause headaches, nosebleeds, loss of smell and trouble swallowing when it’s snorted. Bowel decay is a problem that results from swallowing cocaine. If you inject cocaine, you have the additional health risk of getting HIV or hepatitis.
Another danger is that you don’t know what street dealers do to cocaine. Some of them mix it with other drugs, talcum powder, flour or cornstarch to make more money off the stash of cocaine they have. Cocaine is also more deadly when mixed with other drugs.
The high that cocaine provides doesn’t last long, which leads to people using it frequently as their addiction grows. Injecting and smoking provide a high that lasts 5 to 10 minutes, and snorting gives a 15- to 30-minute high. The crash after using cocaine is unpleasant to go through, so many people will take another dose.
It’s easy to feel trapped in this cycle no matter how badly you want to quit. Addiction is tough to go through, so don’t beat yourself up. You can sign up for a drug rehab program to end the painful cycle of using cocaine. Compassionate professionals will help you manage the uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms, and doctors can give you medications during detox to ease withdrawal symptoms if needed.
Rehab is necessary for treating cocaine addiction because the drug has a strong grip on users. The withdrawal symptoms are challenging to handle without the help of medical professionals. One of the signs of addiction is being unable to quit the drug on your own. Many people in rehab have said that they’ve tried to quit numerous times but couldn’t. It was only once they enrolled in rehab that they could finally stop using cocaine.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is effective in treating the psychological side of addiction. Most rehab centers use cognitive behavioral therapy as the main part of treatment for cocaine addiction. Optional therapies that might be included in your treatment plan are holistic therapy, recreational therapy, motivational interviewing, 12-step treatment and dialectical behavior therapy. EMDR is another type of therapy that some rehab centers offer to treat addiction.
Examples of holistic therapies common at rehab centers are meditation, music, art and yoga. Green Mountain Treatment Center and New Freedom Academy are rehab centers that offer holistic therapy for addiction treatment. They also use cognitive behavioral therapy, 12-step treatment and other evidence-based therapies.
Cognitive behavioral therapy teaches you how your thoughts and emotions impact your actions. It also helps you change these thoughts, emotions and behaviors into more positive ones supportive of your well-being. In addition, CBT is a goal-oriented type of therapy. Having goals to work toward help you avoid using cocaine or other drugs again.
If you have unresolved trauma or grief, this contributes to your addiction. When a therapist works with you to put together an addiction treatment plan, they may include trauma and grief therapy if you have these issues.
Some people who have cocaine addiction also have another mental health disorder like borderline personality disorder or clinical depression. Co-occurring disorder treatment, as offered at Green Mountain Treatment Center and New Freedom Academy, is important for a successful recovery. Just as unresolved trauma can make you more susceptible to using drugs, a mental disorder increases the likelihood that you’ll use drugs.
If you’ve found out that your loved one is using cocaine, you should research the effects and dangers of cocaine use. Then, stage an intervention for your loved one and explain the important information you’ve learned to help them realize that they have a problem and need to seek treatment. Remind them that you love them although you can’t support their cocaine use.
During the intervention, include any family members and close friends of your loved one who are worried about them. If anyone has been negatively affected by your loved one’s cocaine use, then they are allowed to share how it has harmed them and makes them feel. Make sure everyone communicates their feelings in “I” statements to avoid causing your loved one to feel defensive. For instance, you would want to say, “I felt hurt when you lied to me in order to get money for cocaine,” instead of saying, “You hurt me when you lied to me in order to get money for cocaine.”
Be patient and remember that cocaine addiction interferes with a person’s ability to think clearly. Your loved one might not seek treatment the first time you bring up the problem. Don’t give up on them. However, it’s also important that you don’t become too consumed with trying to get them to enroll in rehab either. You’ll harm your own health if you get too preoccupied with their addiction. Look after your health and well-being too. In some cases, a loved one’s addiction becomes so stressful that you may need to talk to a therapist for guidance in managing the overpowering emotions.
If you were using another drug, such as alcohol or marijuana, then those drugs can be triggers for a cocaine craving during abstinence from cocaine. When you quit cocaine, you must abstain from the other drugs you were using to help prevent a relapse.
You’ll also need to enroll in a drug rehab program to overcome your physical and psychological dependence on cocaine. Choose a rehab center that uses cognitive behavioral therapy and other evidence-based clinical therapies. Once you’ve completed a drug rehab program, go through aftercare planning to maintain sobriety as you transition back into day-to-day life. Be aware that you may have to make changes in who you are around when you finish rehab to avoid relapsing. Avoid places you associate with cocaine if possible to reduce your chance of relapsing.
One of the most important steps in overcoming cocaine addiction is to never give up on yourself. No matter how good a therapist or rehab center is, they can’t know for certain if you’ll relapse or not. Relapse is a possibility, but what matters is that you quit the drug again and go back to rehab if necessary. The chance of relapse is greatly diminished when you stick to an outpatient or aftercare plan program for a year. Your sobriety has a chance to become a stronger habit once you’ve gone a year without using the drug.
You can enroll in inpatient, outpatient or partial hospitalization rehab. It depends on the severity of your addiction. Professionals may recommend an inpatient program for cocaine addiction because of how addictive the substance is. An inpatient rehab program lasts 30 to 90 days. You stay at the rehab center where you can be monitored by medical professionals and safely kept out of environments where you would have access to cocaine.
Once you’ve completed inpatient rehab, your treatment team may recommend dropping down into a long-term outpatient program to maintain sobriety. Outpatient programs typically meet 9 to 20 hours a week. Partial hospitalization is an in-between option. You don’t live at the rehab center as you would in an inpatient program, but it requires a great deal of your time. Partial hospitalization rehab programs meet four to six hours per day, five to seven days a week.
Whether you’ve been using cocaine for a few months, a year or several years, you can overcome the addiction. It’s normal to feel some fear in enrolling in rehab, but you will be happy that you did. You will regain a sense of control over your life. You will also restore your health and improve your mood. Be open and honest during rehab to receive the best help possible in overcoming addiction and setting yourself up for a happier life.
If you want to visit one of our New England drug rehab centers, please contact us at Granite Recovery Centers. Our experts will work with you to find a high-quality treatment option that meets your needs. We strive to provide a holistic level of treatment with evidence-based care, giving you the help necessary to regain your sobriety for good.

| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 1 hour | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| .AspNetCore.Cookies | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| .AspNetCore.CookiesC1 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| .AspNetCore.CookiesC2 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| .AspNetCore.CookiesC2 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| .AspNetCore.CookiesC3 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| .AspNetCore.CookiesC3 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| AspNetCore.Cookies | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| AspNetCore.CookiesC1 | 11 months | This cookie is installed by BayMark Health Services, Inc. The cookie is used to maintain persistence with ChatGPT sessions. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie records the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | CookieYes sets this cookie to record the default button state of the corresponding category and the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | The website's WordPress theme uses this cookie. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| wpEmojiSettingsSupports | session | WordPress sets this cookie when a user interacts with emojis on a WordPress site. It helps determine if the user's browser can display emojis properly. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| yt-player-bandwidth | never | The yt-player-bandwidth cookie is used to store the user's video player preferences and settings, particularly related to bandwidth and streaming quality on YouTube. |
| yt-player-headers-readable | never | The yt-player-headers-readable cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences related to video playback and interface, enhancing the user's viewing experience. |
| yt-remote-cast-available | session | The yt-remote-cast-available cookie is used to store the user's preferences regarding whether casting is available on their YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-cast-installed | session | The yt-remote-cast-installed cookie is used to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-fast-check-period | session | The yt-remote-fast-check-period cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences for embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-session-app | session | The yt-remote-session-app cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences and information about the interface of the embedded YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-session-name | session | The yt-remote-session-name cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY | never | The cookie ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY is used by YouTube to store the last search result entry that was clicked by the user. This information is used to improve the user experience by providing more relevant search results in the future. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _uetsid | 1 day | Bing Ads sets this cookie to engage with a user that has previously visited the website. |
| _uetvid | 1 year 24 days | Bing Ads sets this cookie to engage with a user that has previously visited the website. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to display advertisements when either on Facebook or on a digital platform powered by Facebook advertising after visiting the website. |
| _ga | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to calculate visitor, session and campaign data and track site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognise unique visitors. |
| _ga_* | 1 year 1 month 4 days | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store and count page views. |
| _gat_UA-* | 1 minute | Google Analytics sets this cookie for user behaviour tracking. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Google Tag Manager sets the cookie to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _gid | 1 day | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store information on how visitors use a website while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the collected data includes the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| _hjSession_* | 1 hour | Hotjar sets this cookie to ensure data from subsequent visits to the same site is attributed to the same user ID, which persists in the Hotjar User ID, which is unique to that site. |
| _hjSessionUser_* | 1 year | Hotjar sets this cookie to ensure data from subsequent visits to the same site is attributed to the same user ID, which persists in the Hotjar User ID, which is unique to that site. |
| _hjTLDTest | session | To determine the most generic cookie path that has to be used instead of the page hostname, Hotjar sets the _hjTLDTest cookie to store different URL substring alternatives until it fails. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __ctmid | 1 month | CallTrackingMetrics sets this cookie to determine the advertising channel that led a visitor to the website and also show the tracking phone number that corresponds to that channel. |
| fr | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to show relevant advertisements by tracking user behaviour across the web, on sites with Facebook pixel or Facebook social plugin. |
| MUID | 1 year 24 days | Bing sets this cookie to recognise unique web browsers visiting Microsoft sites. This cookie is used for advertising, site analytics, and other operations. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | doubleclick.net sets this cookie to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to measure bandwidth, determining whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| VISITOR_PRIVACY_METADATA | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's cookie consent state for the current domain. |
| YSC | session | Youtube sets this cookie to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ct213024 | session | Description is currently not available. |
| ENTERPRISE_SESSION | 7 days | Description is currently not available. |
| guest | 1 month | No description available. |
| JOTFORM_SESSION | 1 month | No description available. |
| MSPTC | 1 year 24 days | Description is currently not available. |
| userReferer | 1 month | No description available. |